Diadynamic currents are also called Bernard’s currents based on a sine wave with a frequency of 50Hz. Due to the ease of generation of this current shape, they have been known almost from the beginning of electrotherapy, and their influence on the human body has been thoroughly studied.
Parameters and waveform of diadynamic currents
Diadynamic currents are based on a sine wave with a frequency of 50Hz. Several types of diadynamic currents are commonly applied, which differ in shape and order of the half-sine waves.
They include:
| Current type | Current shape |
| MF | upper half-sine waves with a frequency of 50Hz |
| DF | upper and inverted (straight) lower half-sine waves with a frequency of 50Hz |
| RS | phase I – 1s of DF waveform, phase II – 1s of rest phase |
| CP | Phase I – 1s of MF waveform, phase II – 1s of DF waveform |
| LP | phase I – DF waveform while its every second half is modulated by a half-sinusoidal waveform with a period of 10s, phase II -10s of MF waveform |
| MM | phase I – MF waveform modulated by a half-sinusoidal waveform with a period of 10 s, phase II – 10 s rest phase |
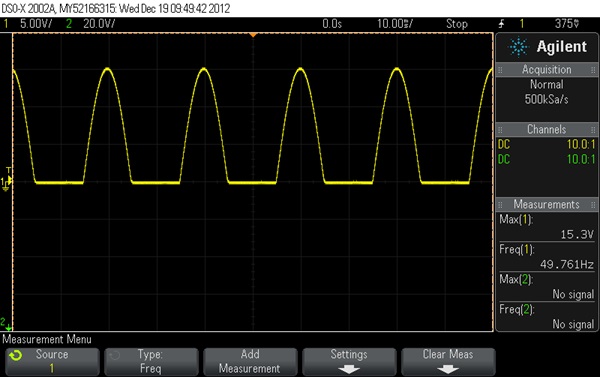 Diadynamic current MF
Diadynamic current MF
Diadynamic currents are unidirectional currents, what’s more, until recently, they were applied with the superposition called base – ie the initial direct current polarization. Currently, because of the studies that have not confirmed the effectiveness of this solution, the base has been withdrawn from the application.
Effect and application of diadynamic currents
Impact of diadynamic currents:
- analgesic effect
- stimulation of blood circulation
- improvement of tissue tropism
- alteration of the muscle tissue excitability
The analgesic effect of diadynamic currents may be also seen as consistent with the gate control theory. Stimulation of endorphins release is another factor triggering off an analgesic effect. Especially DF, CP and LP waveforms exhibit the analgesic effect. In the treatment of pain syndromes, a particular sequence is recommended:
DF 2 min – MF 1 min – CP or LP till the end of the procedure 8 min
Diadynamic currents also cause a strong vascular reaction in the form of hyperemia. This factor is important in the treatment of posttraumatic and peripheral circulatory disorders. Vascular reaction mechanism is based on the stimulation of nerve endings. In order to elicit vascular reaction also the following sequence may be applied:
DF 2 min – MF 1 min – CP or LP to the end of procedure 8 min
Diadynamic currents affect the alteration of the muscle tissue excitability. MF current (with the frequency of 50 Hz) causes hypertonia. DF current (with the frequency of 100 Hz) results in reduction of muscle tension. Applying alternately MF and DF waveforms we obtain isometric muscle gymnastics which results in:
- Reduction of muscle tone
- Muscle hyperaemia
Conclusions:
Such a sequence is nothing but the CP waveform. LP waveform is very similar and it gives much the same results. Segmentary application of diadynamic currents may affect the distant tissue sites.
Method of performing treatment with diadynamic currents
The analgesic effect of diadynamic currents is based on determining a limit at which the current flow is becoming painful. By reducing the current value to a level below the threshold of pain and carrying out only 30s treatment procedure we may obtain the effect of increased pain tolerance. A series of treatments may relieve symptoms lasting for up to several days. Treatments are especially effective when dealing with not very severe pain, but disruptive in nature due to its chronicity.
While carrying out treatment with the application of diadynamic currents we should be aware of the fact that they are unipolar currents. This entails both care about the cleanliness of the electrodes and pads as well as the need of current value control to avoid skin burns under the electrodes.
Diadynamic currents are based on the low frequency waveform which results unfortunately in shallow penetration into the tissue in the case of placement the electrodes next to each other.
At present, there are many other currents, which are more sophisticated as well as safer for the patient and easier to apply such as interferential currents.
Read more about electrotherapy:
Comparison between TENS and EMS currents
