Magnetotherapy is a physical method, under which several clinical studies were conducted. This study concerns the stimulation of collagen synthesis in an animal model.
Abstract
Magnetic field affecting living organisms has the influence on their functions. Physical therapy focuses on interactions that may favorably influence the processes occurring in the body. One of described effects of the magnetotherapy is the synthesis of collagen. Collagen is the substance that provides flexibility in our tissues. Collagen is an essential element of joints. Magnetotherapy is a convenient method of application due to the fact that magnetic field penetrates freely through clothing and body.
Aim
The aim of the study was to evaluate the magnetic filed influence on the synthesis of type II collagen. The study was conducted in an animal model.
Method
The study was published in the International Ortopaedics journal in 2011. The original name of the study is “Pulsed electromagnetic field therapy results in healing of full-thickness articular cartilage defect”.
The study was carried out on 12 adult rabbits, where 6 of them were randomly assigned to a research group, while another 6 constitute a control group. All rabbits underwent surgery to remove a part of hyaline cartilage with a diameter of 3.5 mm from the right knee joint. The place of tissue removal was filled with the calcium-phosphate scaffold. Then, the experimental group was subjected to the influence of the electromagnetic field. For this purpose, electromagnetic field with a frequency of 1 Hz and sinusoidal waveform was applied. The field was applied by the use of a solenoid applicator for a period of six weeks for 1 hour per day. After the experiment, the material for a research was collected. In the case of control group the place of hyaline cartilage removal was filled with fibrous tissue or fibrous cartilage. Both in the case of macroscopic and microscopic observation, the place of filling differed histologically from the surrounding tissue. In the case of research group the place of tissue removal was completed with hyaline cartilage containing type II collagen. This place, macroscopically and microscopically, did not differ from the surrounding tissue. The place of tissue removal could be identified only on the basis of characteristic reconstruction of subchondral layer in the treatment area – magnetotherapy had a positive impact on the restoration of tissue structure.
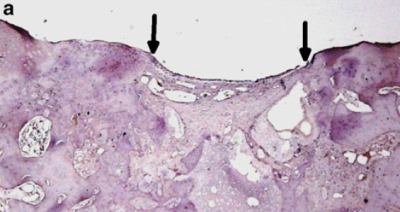
Research results for the presence of type II collagen in the control group – immunochemical method. The area pointed out by arrows indicates the place of deliberate damage. In the figure, there are no visible elements indicating the presence of type II collagen within the damage area. |
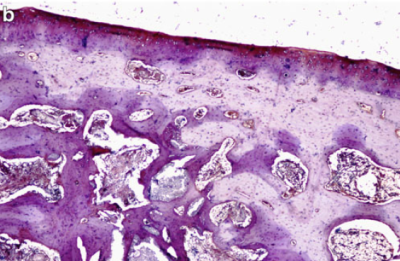
Research results for the presence of type II collagen in the research group – immunochemical method. It is impossible to indicate the area of damage. In the figure, the tissue does not differ from healthy tissue. |
Conclusions
Magnetic field with selected parameters proved to be successful in rebuilding hyaline cartilage and synthesis of type II collagen in the study conducted in an animal model. Magnetotherapy is effective for the reconstruction of damaged joint parts.
